


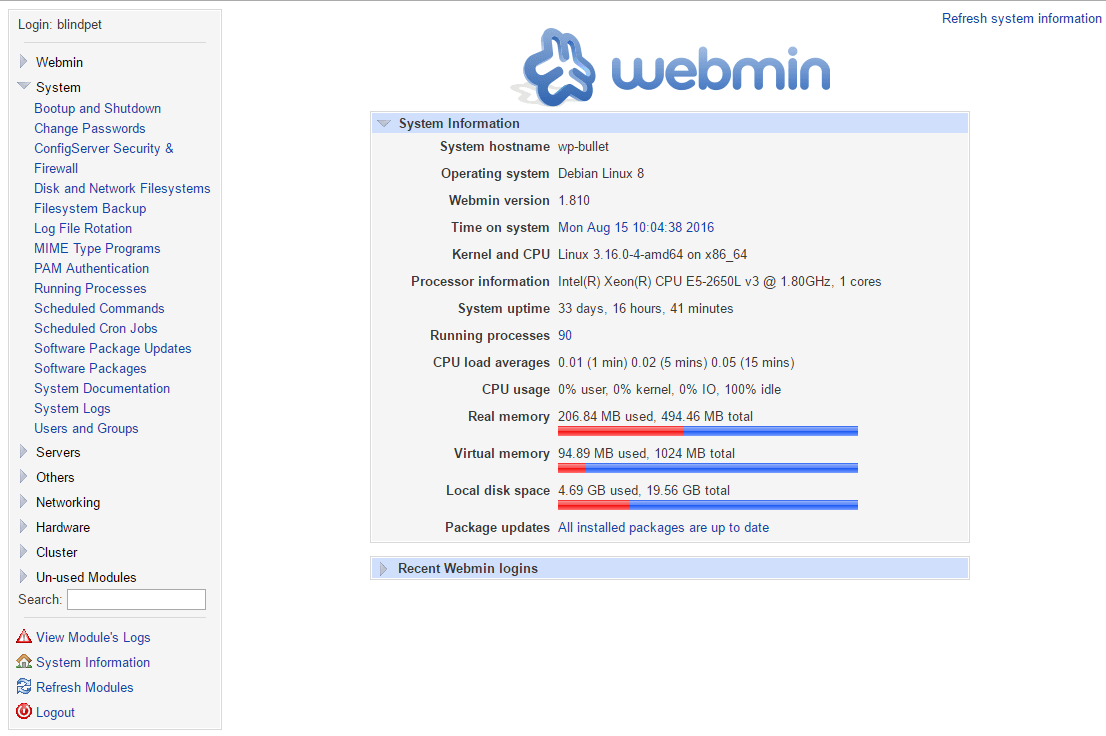
Note: When logging in for the first time, you will see an “Invalid SSL” warning. Navigate to your_domain:10000 in your web browser, replacing your_domain with the domain name pointing to your server’s IP address.

Let’s replace it with a valid certificate from Let’s Encrypt. Webmin is already configured to use HTTPS, but it uses a self-signed, untrusted certificate. Step 2 - Adding a Valid Certificate with Let’s Encrypt Next, you’ll secure access to Webmin by adding a valid certificate. Note: Assuming you installed and enabled ufw during the prerequisite step, you will need to run the following command in order to allow Webmin through the firewall: sudo ufw allow 10000įor extra security, you may want to configure your firewall to only allow access to this port from certain IP ranges. Root password, or as any user who can use sudo. Once the installation finishes, you’ll be presented with the following output: Output. Then install Webmin: sudo apt install webmin Next, update the list of packages again in order to include the now-trusted Webmin repository: sudo apt update If you had used nano to edit, you can exit by pressing CTRL+X, Y, then ENTER. Then add this line to the bottom of the file to add the new repository: /etc/apt/sources.list. Here, you’ll use nano: sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list Next you will add this repository to your /etc/apt/sources.list file, while referencing your newly converted file you just acquired in the previous step.
gpg file, the gpg -dearmor command is necessary. This downloaded key is the same key that was used by the creator of Webmin to sign the package, and you will use this key to verify the package’s authenticity. In order for your system to trust this new repository, first, you’ll download Webmin’s PGP key and then convert it to a format that apt can use to verify files: curl -fsSL | sudo gpg -dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/webmin.gpg Then you need to add the Webmin repository so that you can install and update Webmin using your package manager. To configure this, follow these instructions on DNS hosting on DigitalOcean.įirst, update your server’s package index if you’ve not done so recently: sudo apt update A Fully-Qualified Domain Name (FQDN), with a DNS A record pointing to the IP address of your server.As you follow this prerequisite guide, be sure to configure a virtual host. Apache is installed by following our tutorial on How To Install the Apache Web Server on Ubuntu 22.04.Set this up by following our Ubuntu 22.04 initial server setup guide. This server should have a non-root user with sudo privileges and a UFW firewall configured. To complete this tutorial, you will need: You’ll then use Webmin to add new user accounts and update all packages on your server from the dashboard. In this tutorial, you’ll install and configure Webmin on your server and secure access to the interface with a valid certificate from Let’s Encrypt. With Webmin, you can manage user accounts, configure DNS settings, and change settings for common packages on the fly. Webmin is a modern web control panel that allows you to administer your Linux server through a browser-based interface. How To Install Webmin on Ubuntu 22.04 Introduction


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
